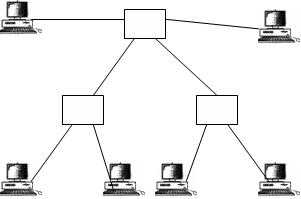
In tree
topology a central 'root' node (the top
level of the hierarchy) is connected to one or more other nodes that are one
level lower in the hierarchy (i.e., the second level) with a point-to-point
link between each of the second level nodes and the top level central 'root'
node. Means nodes in a tree are link to central hub that controls the traffic
to the network but not every device plugs directly to the central controller.
Most of the devices are connect to some secondary hub, which in turn connected
to central hub.
 |
| Tree topology |
A very good example
of tree topology is the cable TV network.
Advantages
·
Scalable
·
More manageable (because, of different levels of network).
Disadvantages
·
Maintenance may b an issue
Mesh Topology
In mesh network
topology every nodes has a dedicated connection to every other nodes. The
dedicated connections in the mesh topology only caries the traffic between two
devices it connects. A fully connected mesh topology has n(n-1)/2 physical channels to link n devices. To manage this much
links very device on the network must need (n-1) input output ports.
 |
| Mesh topology |
Advantages
·
Secure
·
Robust
·
Eliminate traffic problems
Disadvantages
·
Many ports are needed in each device
·
Installation and reconfiguration are difficult
·
Expensive due to huge cabling
Previous : Network Topology Bus and Star
No comments:
Post a Comment